How the YouTube Algorithm Works in 2021


Since its launch in 2005, YouTube has become more than just a platform for users to upload, share, and watch videos. It’s now the second-largest search engine in the world—and a valuable tool for brands and creators alike.
How does YouTube keep those billions of users coming back for more? YouTube uses its algorithms to serve up a never-ending list of relevant content, and always seems to know exactly what users want to watch next.
YouTube has multiple algorithms for ranking content on the home page, search results, and suggested videos. In this article, we’ll explain how YouTube’s algorithms work, and how you can make the most of them.
The first video was uploaded to YouTube in 2005. Fast forward 16 years, and over two billion people log into YouTube every month to find content they love. But the way that YouTube decides what content to serve up has changed significantly over the years.
Before we dive into YouTube’s current algorithms, here is a quick timeline of how YouTube has ranked videos from the platform’s inception through today.
YouTube has been ranking videos based on view count since day one. The platform would suggest videos with hundreds of thousands of views to every user, regardless of their interests. With this system in place, creators could refresh the page and use clickbait titles to gain more views.
From 2012 to 2015, YouTube’s primary goal was to keep users on the platform for as long as possible. (That’s still one of their main goals, but additional factors come into play now.) During this period, videos with long watch times were prioritized in recommendations and on the home page.
In 2016, YouTube published a white paper explaining its machine learning-based algorithm for recommending videos.
Using deep neural networks—a.k.a “deep learning”—YouTube tracks viewers’ history and perceived satisfaction to generate a personalized stream of recommendations.
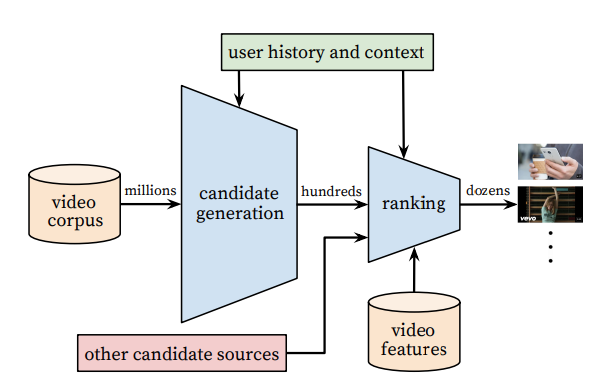
While YouTube hasn’t released the technical details of the algorithm, here’s a brief overview of how it works:
1. YouTube looks at the user’s view history to develop a list of recommended videos (the “candidate generation” funnel)
2. In the “ranking” funnel, the videos are assigned a score based on relevance and a variety of other factors. Then, the videos are listed from highest to lowest score and shown to the user
This machine learning process is likely still a major part of YouTube’s recommendation algorithm as their overarching goal remains viewer satisfaction. Viewer satisfaction is measured through survey responses, and engagement signals, including viewers’ likes, dislikes, and ‘not interested’ clicks.

YouTube outlines the four Rs of its platform as follows:
1. Remove: YouTube prioritizes removing content that violates their policy as swiftly as possible.
2. Raise Up: As viewers are looking for content related to breaking news, and other up-to-date information, YouTube works to “raise up authoritative voices” so the content that most accurately reflects their search intent is surfaced.
3. Reward Trusted Sources: YouTube’s goals include rewarding their most “trusted, eligible creators and artists.”
4. Reduce the Spread: When “content that brushes right up against” YouTube’s policy line is published, they will work to reduce the spread, or reach, of that content.
The four Rs became more prominent in 2017, when the platform began redirecting users seeking extremist propaganda to playlists debunking those ideas. YouTube also began prioritizing expert voices and news sources when users search for videos about current events.
In 2019, YouTube began systematically removing “borderline” content, meaning content that comes close to violating the Community Guidelines and spreads harmful misinformation. YouTube also announced over 30 changes designed to “raise authoritative voices on YouTube and reduce the spread of borderline content and harmful misinformation.”
YouTube is now the second largest search engine, outranked only by its parent company, Google. YouTube sees over three billion searches per month—more than Bing, Yahoo, AOL, and Ask.com combined.
To build your brand visibility and drive engagement, it’s crucial to understand the latest YouTube trends and emerging SEO best practices. Here’s how YouTube ranks videos on the search engine results page (SERP), and how creators and brands can optimize their videos for YouTube SEO.
The two main SERP ranking signals for YouTube are:
1. Keyword relevance based on metadata (Title, description, and keywords)
2. Engagement metrics (Watch time, likes, comments, etc.)
YouTube looks at how well your titles, descriptions, and content match a user’s search query.
When it comes to engagement metrics, watch time and recency are two of the biggest factors in SERP ranking for video. YouTube also factors in users’ watch history; how many videos have users watched from your channel, and when did they last watch videos on the same topic?
Additional ranking signals include:
All in all, videos that answer users’ questions and hold viewers’ interest will benefit the most from YouTube’s ranking algorithm.
To make the most of YouTube’s SEO algorithm, creators and brands need to optimize metadata. Metadata includes your video’s title, description, and tags.
“Like Google’s search engine, search on YouTube strives to surface the most relevant results according to keyword queries. Videos are ranked based on a variety of factors including how well the title, description, and video content match the viewer’s query.”
SEO tools like Ahrefs and Ubersuggest can help creators identify popular searches and related keywords. Keyword-rich titles and descriptions make it more likely that videos will show up in relevant searches.
YouTube recommends writing one- or two-paragraph descriptions that “give an overview of your video using natural language—not just a stream of keywords.” Include the most important keywords in the beginning of your description, and include your primary keyword in your video title.
The description field helps viewers find your video and decide if they want to watch it. The first few lines of your description will show up on the SERP and on the video page before the “Show more” link. You can add additional information (and keywords) below the “Show more” break.
Your video title and thumbnail can also impact your ranking. A great thumbnail means more people will click on your video from the SERP, which boosts your views and tells YouTube that your video fits the query. Your thumbnail should accurately reflect your video’s content; otherwise, it can backfire and hurt your ranking.
“When viewers click into your video and stay to watch through, this lets YouTube know that the viewer is enjoying your content. However, if your thumbnails and titles don’t deliver on their promise of what’s in the video, viewers tend to leave almost immediately, which can limit your discoverability on YouTube. The longer you can keep people watching on YouTube because of your content, the more your content may get surfaced.”
You can also add tags to your videos. Tags help viewers find your content; however, they play a minimal role in your video’s discovery. Your video’s title, thumbnail, and description are more important pieces of metadata when it comes to SEO and driving traffic.
YouTube suggests videos to users in the “Suggested Videos” sidebar on the right side of the watch page, below videos on the mobile app, and as the next video in autoplay.
How does YouTube decide which videos to recommend to users?
According to YouTube, the platform “tries to match each viewer to the videos they are most likely to watch and enjoy.” The goal is to keep users on YouTube for as long as possible, which naturally results in them seeing more ads.
This is where the deep learning algorithm we covered earlier comes into play. The algorithm ranks videos based on their performance, then matches them with potential viewers based on several recommendation factors. You can think of it as a matchmaking game that aims to partner each viewer with the content that best answers for their search intent, and holds their attention—it has to be more than a pretty thumbnail!
Recommendation factors include:
To increase the likelihood a viewer will watch more than one of your videos in a row, YouTube recommends the following:
To see which videos bring viewers to your channel from “Suggested Videos,” take a look at the “Traffic Sources” report in your YouTube Analytics dashboard.
The “Trending” page on YouTube is a feed of new and popular videos in a user’s country. You can find the Trending page by clicking “Explore” in the sidebar, then clicking on “Trending”.
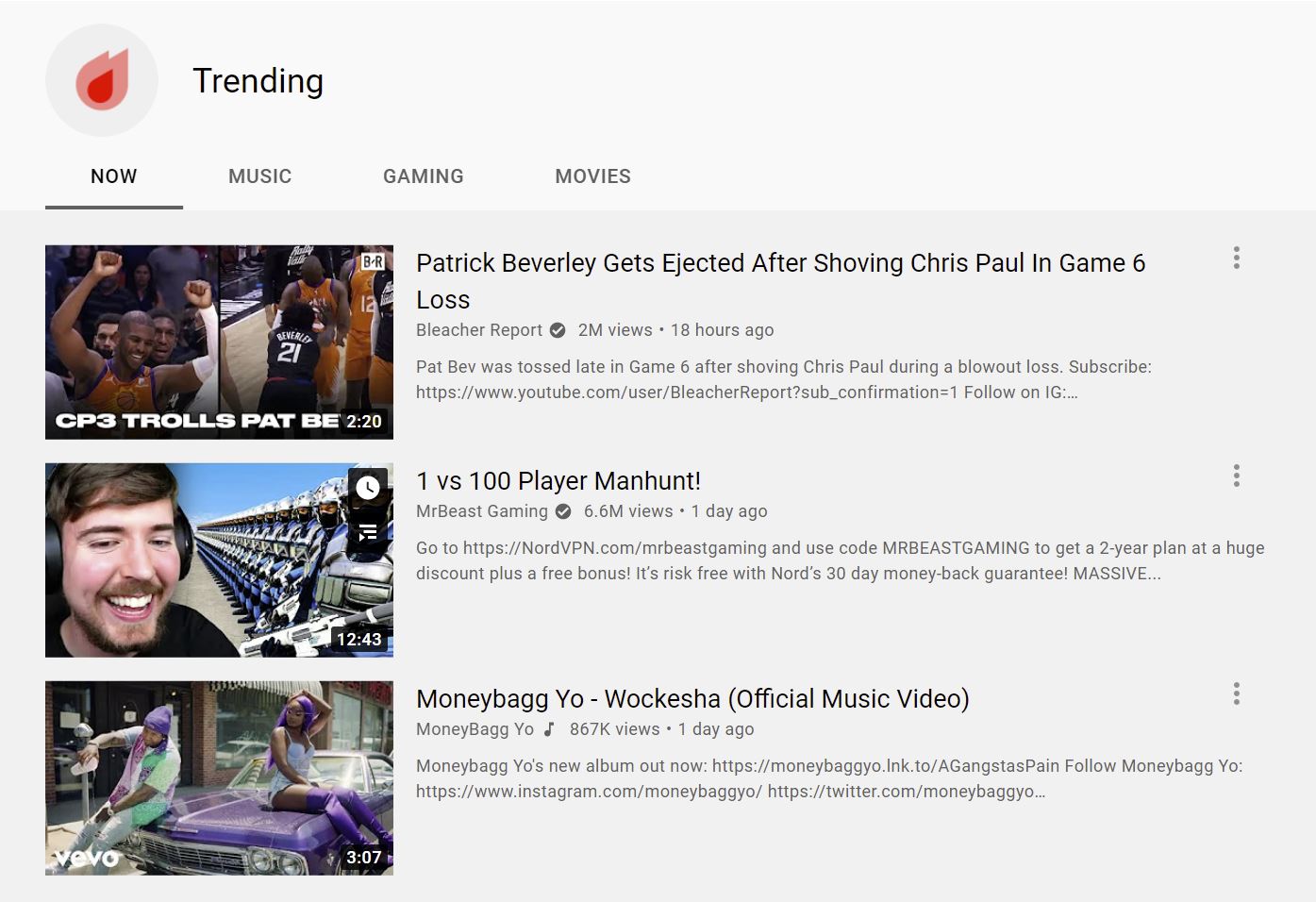
Videos are split into four categories:
Unlike suggested videos, trending videos are not tailored to each user. Instead, to determine which videos are trending, YouTube considers popularity (view count) and novelty (view velocity).

YouTube’s primary source of revenue is advertising, and they understand that there is an abundance of content on their platform that most brands won’t want their ads to show alongside. With this in mind, they have created advertiser-friendly content guidelines for Creators who want their videos to be ad-eligible. Their channel is also required to follow YouTube monetization policies, which include YouTube Community Guidelines, and Google AdSense program policies.
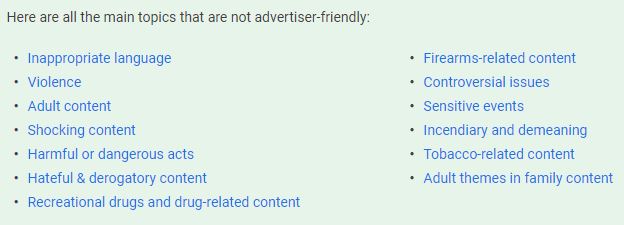
YouTube notes that context does come into play when determining if a video is ad-eligible.
“Artistic content such as music videos may contain elements such as inappropriate language, references to soft drug usage, or non-explicit sexual themes, and still be suitable for advertising.”
As for which of those YouTube-vetted, advertiser-friendly videos your ads will show before, during, or after? YouTube notes:
“YouTube Ads uses Google data to match your message to the right people at the right moment.”
When you create a YouTube Ads campaign—which is set-up and managed through a Google Ads account—you will have the opportunity to define the audiences you’re most interested in reaching.
Last but not least, how can creators track how well their videos are performing?
YouTube offers a robust analytics dashboard that tells creators “who’s watching, what they like to watch, and which videos could make you the most money.”
To track whether the YouTube algorithms show your videos to users, use the reports in the “Reach” tab. Some of the most helpful YouTube analytics reports include:
By optimizing your videos using the tips we shared today, and keeping an eye on these reports and metrics, you will be well on your way to making the YouTube algorithms work for you.
