Tracking & Measuring Micro Conversions

There’s an over-dependence on last-click attribution. It’s become far too easy to immediately want to identify where a sale (or any other conversion, for that matter) directly came from instead of focusing on the path taken to get there. Last-click is important, but it shouldn’t devalue the significance of micro conversions.
Despite the name, micro conversions can represent a big source of valuable information for digital retailers.
Understanding what customers are doing on your website is paramount. Behavioral data, even when it fails to result in a sale, can still be incredibly informative. But that hasn’t stopped such a large emphasis from being placed on macro conversions.
Things like sales conversions are the types of key metrics many sites tend to focus on most. And rightfully so. They are the most easily attributable (i.e. last-click) and often hold direct correlations to specific campaign efforts. Naturally, the “big stuff” tends to trump everything else.
But micro conversions should be vying for much of your attention as well.
For the sake of being thorough, let’s first define macro conversions and their importance.
To put it simply, macro conversions are sales (in most cases). Turning prospective shoppers into existing customers is really the main objective most digital retailers are pushing for.
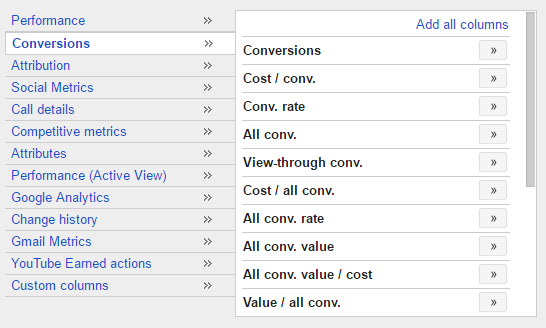
But macro conversions can be anything from downloading a piece of content to filling out a lead form. It really just depends on the type of business and how its key objectives are defined.
Macro and micro conversions can be broadly split into two major categories:
Improving the health of your primary goals, or macro conversions, is always of the utmost importance. But tracking and measuring your micro conversions can be a direct contributor to the well-being of those macro conversions.
Micro conversions are the specific touch points and movements users make as they traverse a website – which will hopefully lead to the completion of a macro conversion.
It’s pretty easy to understand when comparing it to the customer buying process.
While macro conversions are typically the main objective, they are often only relevant during the purchasing stage. Everything else? Everything else is a potential micro conversion.
It’s not often that users go directly to a site’s product page and immediately make a purchase. In fact, it’s unlikely that most visitors will complete a macro conversion at all; it’d be unrealistic to think most of them would. People usually browse, check out other products, and really just hit different touch points as they make their way through the buying process.
Being able to make sense of the “path” of such buying processes, though – i.e. measuring what they engage with and how they engage with it – that can supply you with a nuanced understanding of how to improve conversion optimization.
While primary or macro conversions will vary depending on a business’ goals, micro conversions can be immensely representative of potential macro conversion indicators.
The first step is defining what constitutes or qualifies a micro conversion. It’s going to be different for every site so you’ll need to determine which micro conversions are most valuable to you.
If someone goes to your “Contact Us” page, it’s likely they’re just looking for a phone number or checking to see where your company is located. If you only have basic information on the contact page, you may not care who goes there. If it’s not providing any sort of “big picture” value to you, then it may be worth focusing on other tracking points.
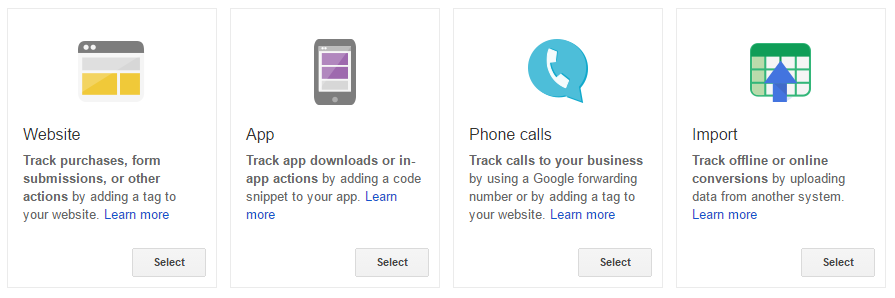
So what kinds of micro conversions are there and which ones should you be tracking? A good way to figure this out is trying to work backwards. Start with your macro conversions (sales, email subscribes, etc) and identify the major touch points that lead up to them.
Some types of micro conversions:
Looking at cart abandoners or product page views isn’t a revolutionary tracking metric by any means. But the more data you have, the more you have to utilize.
By itself, a single micro conversion is unlikely to be indicative of anything. But a band of them measured together can be telling when trying to gauge how close an individual may be toward completing a purchase.
Analyzing traffic is one thing. Segmenting that traffic is another. Take the collective total of all site visitors and you’ll have trouble putting a face to them or figuring out what they’re doing. Measuring various micro conversions help understand not only how you should be segmenting traffic, but what that traffic is doing and how you might be able to better engage them.
Measuring micro conversions offers a holistic understanding of the customer experience.
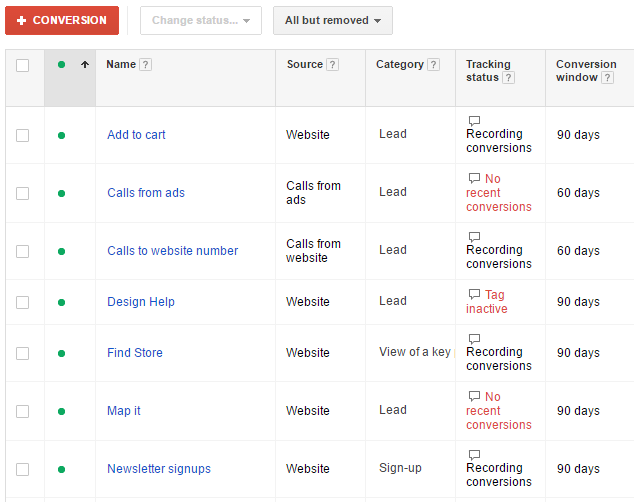
Sites commonly have several kinds of micro conversions, so determining which ones you want to track will be largely dependent on the different goals you have set up.
There are two ways to track micro conversions in Google Analytics. You’ll need to set your micro conversions as events or as goals.
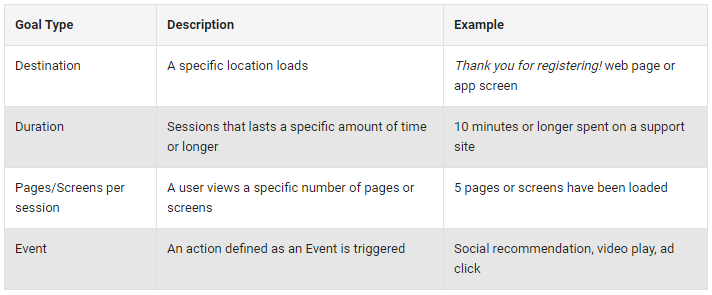
From there, you can start to garner data sets and start to track user flow. Tracking user flow will show you where people are coming from, what pages they’re landing on, and where they end up afterward.
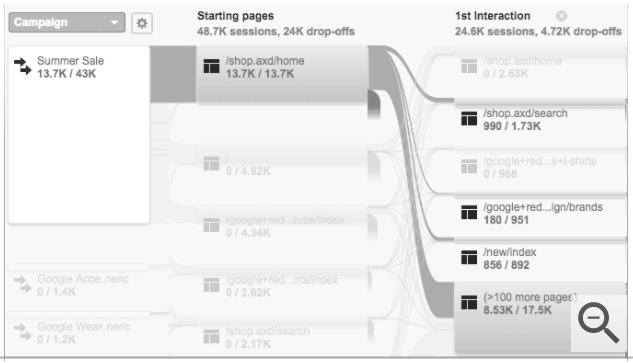
Hopefully, patterns will start to emerge. Things like if homepage traffic is coming from organic searches or if social platforms, such as Facebook, are driving people towards particular website actions or objectives.
These are just a few examples of how micro conversions can be tracked.
You can amass all the data you want, but if you aren’t doing anything with it, it’s not going to provide much value. So the big question is, what’s the point?
“Micro conversions can be helpful for retailers with high Average Order Value (AOV) products and long sales cycles” said Adam Harms, Retail Search Manager at CPC Strategy.
long sales cycles” said Adam Harms, Retail Search Manager at CPC Strategy.
Items, like furniture or high-end electronics, are going to have longer sales cycles. Shoppers are generally going to do a lot of research beforehand comparing prices and brands. Keeping an eye on where your brand fits in with that research can be helpful.
“These retailers can gain valuable insights by broadening their perceptions of a conversion to include more steps along the path to a purchase.”
Again, only a small fraction of people are coming to your site to complete a purchase. The rest are coming for any number of reasons. Whether it’s to find out more about a product or read up on your company, they’re there doing something and they’re hitting different touch points along the way.
“Focusing on just the final step of an order is myopic — it’s important to track users along the way to learn what micro conversions make a final purchase more likely.”
